本篇内容主要讲解“C#中获取文件大小问题怎么解决”,感兴趣的朋友不妨来看看。本文介绍的方法操作简单快捷,实用性强。下面就让小编来带大家学习“C#中获取文件大小问题怎么解决”吧!
C# 获取文件大小
直接贴代码吧
/// <summary>
/// 格式化文件大小
/// </summary>
/// <param name="filesize">文件传入大小</param>
/// <returns></returns>
private static string GetFileSize(long filesize)
{
try
{
if (filesize < 0)
{
return "0";
}
else if (filesize >= 1024 * 1024 * 1024) //文件大小大于或等于1024MB
{
return string.Format("{0:0.00} GB", (double)filesize / (1024 * 1024 * 1024));
}
else if (filesize >= 1024 * 1024) //文件大小大于或等于1024KB
{
return string.Format("{0:0.00} MB", (double)filesize / (1024 * 1024));
}
else if (filesize >= 1024) //文件大小大于等于1024bytes
{
return string.Format("{0:0.00} KB", (double)filesize / 1024);
}
else
{
return string.Format("{0:0.00} bytes", filesize);
}
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
throw ex;
}
}上述代码是将文件大小格式化为我们想要的大小。
FileInfo t = new FileInfo(filePath);//获取文件
文件大小 = GetFileSize(t.Length);//这样我们就获取到了文件的大小C# 获取文件占用空间 (绝对准确)
先说一下为什么要用这种极其麻烦的方法来判断文件的占用空间,因为找不到简单的方法。
如果是想算文件夹的占用空间,只需要将里面的文件的占用空间加在一起就可以了。
首先说下文件大小与占用空间的区别
这与是硬盘分区格式有关。
大小是文件的实际大小,而占用空间是占硬盘的实际空间,以FAT32格式为例,硬盘的基本存储单位是簇,在FAT32中一簇是4KB 那么,也就是说即使文件只有1个字节,在硬盘上也要占到4KB的空间 如果文件是4KB零1个字节,那就要占用8KB的空间,以此类推 结论: 大小是文件的实际大小,而占用空间是占硬盘的实际空间。
如图(我这里一簇是4kB)
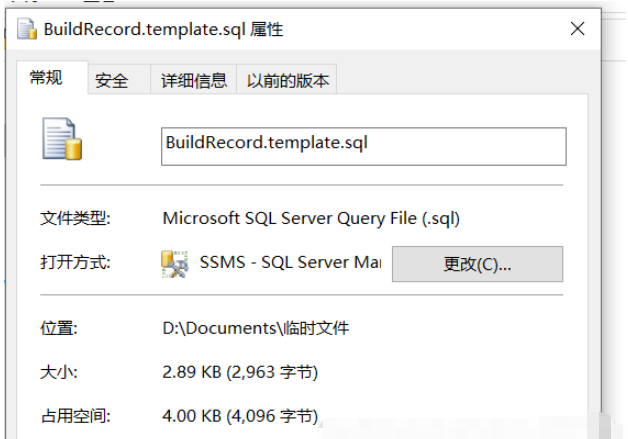
计算思路
所以,要想获得占用空间,就需要先获得文件的大小,然后就可以通过把簇补全即可算出文件的占用空间。而获取文件大小的方法很简单,其代码如下。
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(filePath);
Console.WriteLine(fileInfo.Length);但是通过这种方法计算出的数据并不准确
为什么会不准确呢?因为有很多不正常的文件,那些文件的大小是大于文件占用空间的,例如:
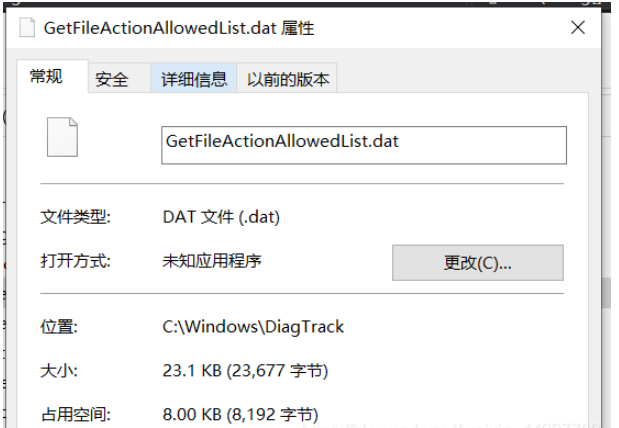
而这种情况通过上面的那一段代码求出的文件大小为23677字节,然后补全簇之后得出的结果一定是大于文件大小的,怎么也不可能得出8192字节(8KB),所以,通过这种方法得出的结果是不准确的。
为什么会出现这种情况?根据硬盘存储空间的规则可以得出,占用空间一定是比其文件大小要大的。那么,只有一种可能,那就是该大小并不是文件的实际大小,它是假的(也有可能是文件管理系统中的某个未知的压缩功能导致的)。
获取文件的实际大小
要想获取一个文件的实际大小,需要调用底层的windows API,这些api都是通过C++来编写的。
里面就有一个可以用来获取文件的实际大小:GetCompressedFileSize()方法。
该方法的说明文档如下:(为什么里面的方法名多了个A,我也不知道为什么,反正可以拿来用)
所以获取文件实际大小的方法如下:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string name = @"D:Documents est.zip";
//用来获取高位数字(只有在读取超过4GB的文件才需要用到该参数)
uint h = 0;
//用来获取低位数据
uint l = GetCompressedFileSize(name, ref h);
//将两个int32拼接成一个int64
ulong r = ((ulong)h << 32) + l;
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(name);
Console.WriteLine(fileInfo.Length);
Console.WriteLine(h);
Console.WriteLine(l);
//最终结果
Console.WriteLine(r);
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
private static extern uint GetCompressedFileSize(string fileName, ref uint fileSizeHigh);然后拿一个正常的文件测试一下
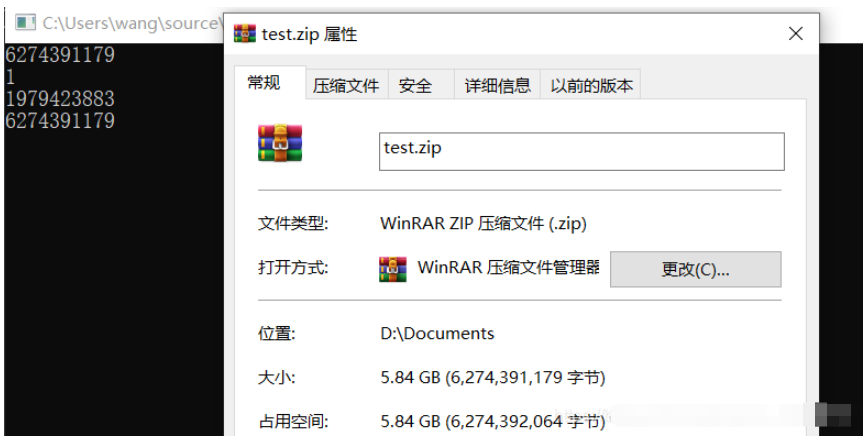
可以看出,字节数是正确的,然后再加上补全簇的算法,一切就正常了。
其代码如下:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string name = @"C:WindowsDiagTrackGetFileActionAllowedList.dat";
//string name = @"D:Documents est.zip";
uint h = 0;
uint l = GetCompressedFileSize(name, ref h);
ulong r = ((ulong)h << 32) + l;
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(name);
Console.WriteLine(fileInfo.Length);
Console.WriteLine(h);
Console.WriteLine(l);
Console.WriteLine(r);
ulong size = GetClusterSize("D:");
if (r%size != 0)
{
decimal res = r / size;
uint clu = (uint)Convert.ToInt32(Math.Ceiling(res)) + 1;
r = size * clu;
}
//最终结果
Console.WriteLine(r);
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
//获取每簇的字节数
private static uint GetClusterSize(string rootPath)
{
//提前声明各项参数
uint sectorsPerCluster = 0, bytesPerSector = 0, numberOfFreeClusters = 0, totalNumberOfClusters = 0;
GetDiskFreeSpace(rootPath, ref sectorsPerCluster, ref bytesPerSector, ref numberOfFreeClusters, ref totalNumberOfClusters);
return bytesPerSector * sectorsPerCluster;
}
//用于获取文件实际大小的api
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
private static extern uint GetCompressedFileSize(string fileName, ref uint fileSizeHigh);
//用于获取盘信息的api
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
private static extern bool GetDiskFreeSpace([MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPTStr)]string rootPathName, ref uint sectorsPerCluster, ref uint bytesPerSector, ref uint numberOfFreeClusters, ref uint totalNumbeOfClusters);最后再看一下那个不正常的文件:
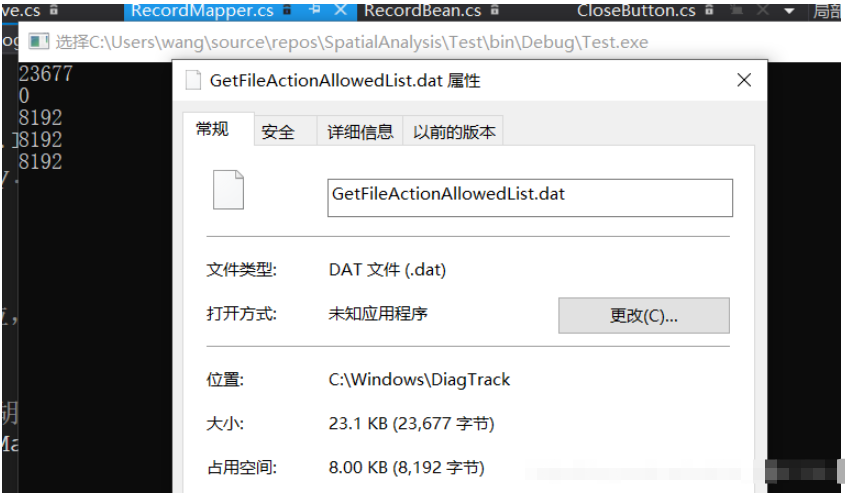
结果8192字节,计算成功。
。。。
。。。
。。。
这个C#也太坑了吧,为了弄一个获取占用空间,我搞了整整一整天。也不知道微软怎么想的,就不能直接给一个获取占用空间方法吗?非地让我们自己算,哎。
后续
有时间为上面的代码加了一点说明,同时也加上了错误处理,修改后的代码如下:
using System;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.IO;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
namespace ConsoleApp1
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
string name = @"目标文件夹路径";
uint h = 0;
uint l = GetCompressedFileSize(name, ref h);
if (l == uint.MaxValue)
throw new IOException("文件读取失败。", new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()));
ulong r = ((ulong)h << 32) + l;
FileInfo fileInfo = new FileInfo(name);
Console.WriteLine("文件大小:");
Console.WriteLine(fileInfo.Length);
Console.WriteLine("高位数据:");
Console.WriteLine(h);
Console.WriteLine("低位数据:");
Console.WriteLine(l);
Console.WriteLine("文件实际大小:");
Console.WriteLine(r);
ulong size = GetClusterSize("D:");
if (r % size != 0)
{
decimal res = r / size;
uint clu = (uint)Convert.ToInt32(Math.Ceiling(res)) + 1;
r = size * clu;
}
//最终结果
Console.WriteLine("文件占用空间:");
Console.WriteLine(r);
Console.ReadKey(true);
}
//获取每簇的字节数
private static uint GetClusterSize(string rootPath)
{
//提前声明各项参数
uint sectorsPerCluster = 0, bytesPerSector = 0, numberOfFreeClusters = 0, totalNumberOfClusters = 0;
GetDiskFreeSpace(rootPath, ref sectorsPerCluster, ref bytesPerSector, ref numberOfFreeClusters, ref totalNumberOfClusters);
return bytesPerSector * sectorsPerCluster;
}
//用于获取文件实际大小的api
[DllImport("Kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto, SetLastError = true)]
private static extern uint GetCompressedFileSize(string fileName, ref uint fileSizeHigh);
//用于获取盘信息的api
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
private static extern bool GetDiskFreeSpace([MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.LPTStr)]string rootPathName, ref uint sectorsPerCluster, ref uint bytesPerSector, ref uint numberOfFreeClusters, ref uint totalNumbeOfClusters);
}
}